Please scroll down for more
Stars
Vs.
Sun & Earth
Click image below for larger viewing & purchasing
Neutron Florida
Neutron stars are incredibly dense remnants of older stars that have blown off their outer gas layers. Many are only as far across as a city. In this cosmic comparison, we see a typical neutron star compared to the gulf coast of the US.
Digital image ©Michael Carroll
Neutron Europe
Neutron stars are incredibly dense remnants of older stars that have blown off their outer gas layers. Many are only as far across as a city. In this cosmic comparison, we see a typical neutron star compared to France and northern Spain.
Digital image ©Michael Carroll
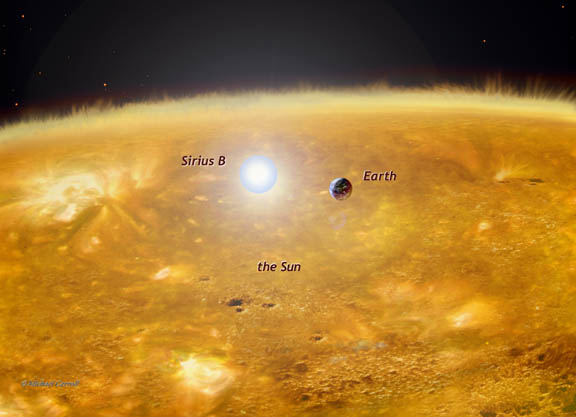
Sirius B
Sirius B, a white dwarf star just 8.6 light-years from Earth, is a little larger than our world, and far smaller than our Sun. It orbits the brightest star in Earth's sky, Sirius A, at a distance equivalent to the distance from our Sun to Uranus. While Sirius B is about the size of Earth, it has nearly as much mass as our our Sun.
Digital image ©Michael Carroll
SIRIUS-RIGEL
The brightest star in Earth's sky, Sirius, is seen here next to our Sun and the blue giant Rigel. Sirius has a small companion star, Sirius B. Rigel forms the left foot in the constellation Orion, and its light is equal to 40,000 suns.
Digital image ©Michael Carroll
RIGEL-BETELGEUSE-ANTARES
The Sun and Rigel are dwarfed by the red supergiants Betelgeuse and Antares. Antares (alpha Scorpii) is the brightest star in the constellation Scorpius.
Digital image ©Michael Carroll
Betelgeuse
Betelgeuse is a red giant, one of the largest stars known. It forms the left shoulder of the constellation Orion. If Betelgeuse was placed at the center of our solar system, its fuzzy edge would extent out well beyond the orbit of Mars.
Digital image ©Michael Carroll